Get the e+ e- thrust basis and the thrust, thrust major and thrust minor scalars.
More...
|
|
| Thrust () |
| | Constructor.
|
| |
|
| Thrust (const FinalState &fsp) |
| |
|
| DEFAULT_RIVET_PROJ_CLONE (Thrust) |
| | Clone on the heap.
|
| |
|
| double | thrust () const |
| |
|
double | thrustMajor () const |
| | The thrust major scalar, 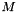 , (thrust along thrust major axis). , (thrust along thrust major axis).
|
| |
|
double | thrustMinor () const |
| | The thrust minor scalar,  , (thrust along thrust minor axis). , (thrust along thrust minor axis).
|
| |
|
double | oblateness () const |
| | The oblateness,  . .
|
| |
|
| const Vector3 & | thrustAxis () const |
| |
|
const Vector3 & | thrustMajorAxis () const |
| | The thrust major axis (axis of max thrust perpendicular to thrust axis).
|
| |
|
const Vector3 & | thrustMinorAxis () const |
| | The thrust minor axis (axis perpendicular to thrust and thrust major).
|
| |
|
|
const Vector3 & | axis1 () const |
| | AxesDefinition axis accessors.
|
| |
|
const Vector3 & | axis2 () const |
| | The 2nd most significant ("major") axis.
|
| |
|
const Vector3 & | axis3 () const |
| | The least significant ("minor") axis.
|
| |
|
Ways to do the calculation directly, without engaging the caching system
|
|
void | calc (const FinalState &fs) |
| | Manually calculate the thrust, without engaging the caching system.
|
| |
|
void | calc (const vector< Particle > &fsparticles) |
| | Manually calculate the thrust, without engaging the caching system.
|
| |
|
void | calc (const vector< FourMomentum > &fsmomenta) |
| | Manually calculate the thrust, without engaging the caching system.
|
| |
|
void | calc (const vector< Vector3 > &threeMomenta) |
| | Manually calculate the thrust, without engaging the caching system.
|
| |
|
virtual | ~AxesDefinition () |
| | Virtual destructor.
|
| |
|
virtual unique_ptr< Projection > | clone () const =0 |
| | Clone on the heap.
|
| |
|
virtual std::string | name () const |
| | Get the name of the projection.
|
| |
|
| Projection () |
| | The default constructor.
|
| |
|
virtual | ~Projection () |
| | The destructor.
|
| |
| bool | before (const Projection &p) const |
| |
| virtual const std::set< PdgIdPair > | beamPairs () const |
| |
| Projection & | addPdgIdPair (PdgId beam1, PdgId beam2) |
| |
|
| ProjectionApplier () |
| | Constructor.
|
| |
|
void | markAsOwned () const |
| | Mark this object as owned by a proj-handler.
|
| |
|
std::set< ConstProjectionPtr > | getProjections () const |
| | Get the contained projections, including recursion.
|
| |
|
bool | hasProjection (const std::string &name) const |
| | Does this applier have a projection registered under the name name?
|
| |
| template<typename PROJ > |
| const PROJ & | getProjection (const std::string &name) const |
| |
| template<typename PROJ > |
| const PROJ & | get (const std::string &name) const |
| |
| const Projection & | getProjection (const std::string &name) const |
| |
| template<typename PROJ > |
| const PROJ & | applyProjection (const Event &evt, const Projection &proj) const |
| | Apply the supplied projection on event evt. More...
|
| |
| template<typename PROJ > |
| const PROJ & | apply (const Event &evt, const Projection &proj) const |
| |
| template<typename PROJ > |
| const PROJ & | applyProjection (const Event &evt, const PROJ &proj) const |
| | Apply the supplied projection on event evt. More...
|
| |
| template<typename PROJ > |
| const PROJ & | apply (const Event &evt, const PROJ &proj) const |
| |
| template<typename PROJ > |
| const PROJ & | applyProjection (const Event &evt, const std::string &name) const |
| |
| template<typename PROJ > |
| const PROJ & | apply (const Event &evt, const std::string &name) const |
| |
| template<typename PROJ > |
| const PROJ & | apply (const std::string &name, const Event &evt) const |
| |
Get the e+ e- thrust basis and the thrust, thrust major and thrust minor scalars.
- Author
- Andy Buckley
The scalar (maximum) thrust is defined as
![\[ T = \mathrm{max}_{\vec{n}} \frac{\sum_i \left|\vec{p}_i \cdot \vec{n} \right|}{\sum_i |\vec{p}_i|} \]](form_119.png)
, with the direction of the unit vector 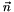 which maximises
which maximises 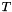 being identified as the thrust axis. The unit vector which maximises the thrust scalar in the plane perpendicular to
being identified as the thrust axis. The unit vector which maximises the thrust scalar in the plane perpendicular to 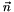 is the "thrust major" direction, and the vector perpendicular to both the thrust and thrust major directions is the thrust minor. Both the major and minor directions have associated thrust scalars.
is the "thrust major" direction, and the vector perpendicular to both the thrust and thrust major directions is the thrust minor. Both the major and minor directions have associated thrust scalars.
Thrust calculations have particularly simple forms for less than 4 particles, and in those cases this projection is computationally minimal. For 4 or more particles, a more general calculation must be carried out, based on the Brandt/Dahmen method from Z. Phys. C1 (1978). While a polynomial improvement on the exponential scaling of the naive method, this algorithm scales asymptotically as 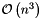 . Be aware that the thrust may easily be the most computationally demanding projection in Rivet for large events!
. Be aware that the thrust may easily be the most computationally demanding projection in Rivet for large events!
The Rivet implementation of thrust is based heavily on Stefan Gieseke's Herwig++ re-coding of the 'tasso' code from HERWIG.
NB. special case with >= 4 coplanar particles will still fail. NB. Thrust assumes all momenta are in the CoM system: no explicit boost is performed. This can be dealt with by appropriate choice of the supplied FinalState.

 1.8.13
1.8.13
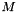 , (thrust along thrust major axis).
, (thrust along thrust major axis).  , (thrust along thrust minor axis).
, (thrust along thrust minor axis).  .
.  Public Member Functions inherited from
Public Member Functions inherited from ![\[ T = \mathrm{max}_{\vec{n}} \frac{\sum_i \left|\vec{p}_i \cdot \vec{n} \right|}{\sum_i |\vec{p}_i|} \]](form_119.png)
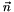 which maximises
which maximises 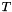 being identified as the thrust axis. The unit vector which maximises the thrust scalar in the plane perpendicular to
being identified as the thrust axis. The unit vector which maximises the thrust scalar in the plane perpendicular to 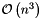 . Be aware that the thrust may easily be the most computationally demanding projection in
. Be aware that the thrust may easily be the most computationally demanding projection in