Public Member Functions |
Protected Member Functions |
Protected Attributes |
Private Attributes |
Friends
Hemispheres Class Reference Calculate the hemisphere masses and broadenings. More...
Detailed DescriptionCalculate the hemisphere masses and broadenings. Calculate the hemisphere masses and broadenings, with event hemispheres defined by the plane normal to the thrust vector, The "high" hemisphere mass,
and the corresponding "low" hemisphere mass, Finally, we define a hemisphere mass difference:
Similarly to the masses, we also define hemisphere broadenings, using the momenta transverse to the thrust axis:
and then a set of the broadening maximum, minimum, sum and difference as follows:
Internally, this projection uses a Thrust or Sphericity projection to determine the hemisphere orientation. Definition at line 56 of file Hemispheres.hh. Constructor & Destructor Documentation
Constructor. Definition at line 60 of file Hemispheres.hh. {
setName("Hemispheres");
addProjection(ax, "Axes");
clear();
}
Member Function Documentation
Non-templated version of string-based applyProjection, to work around header dependency issue. Definition at line 22 of file ProjectionApplier.cc. {
return evt.applyProjection(getProjection(name));
}
Non-templated version of proj-based applyProjection, to work around header dependency issue. Definition at line 28 of file ProjectionApplier.cc. {
return evt.applyProjection(proj);
}
Untemplated function to do the work... Definition at line 34 of file ProjectionApplier.cc. {
if (!_allowProjReg) {
cerr << "Trying to register projection '"
<< proj.name() << "' before init phase in '" << this->name() << "'." << endl;
exit(2);
}
const Projection& reg = getProjHandler().registerProjection(*this, proj, name);
return reg;
}
Add a colliding beam pair. Definition at line 108 of file Projection.hh. {
_beamPairs.insert(PdgIdPair(beam1, beam2));
return *this;
}
Register a contained projection (user-facing version)
Definition at line 157 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. { return declareProjection(proj, name); }
Apply the supplied projection on event evt (user-facing alias).
Definition at line 80 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. { return applyProjection<PROJ>(evt, proj); }
Apply the supplied projection on event evt (user-facing alias).
Definition at line 92 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. { return applyProjection<PROJ>(evt, proj); }
Apply the supplied projection on event evt (user-facing alias).
Definition at line 104 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. { return applyProjection<PROJ>(evt, name); }
Apply the supplied projection on event evt.
Definition at line 74 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. {
return pcast<PROJ>(_applyProjection(evt, proj));
}
Apply the supplied projection on event evt.
Definition at line 86 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. {
return pcast<PROJ>(_applyProjection(evt, proj));
}
Apply the named projection on event evt.
Definition at line 98 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. {
return pcast<PROJ>(_applyProjection(evt, name));
}
Definition at line 146 of file Hemispheres.hh. Return the allowed beam pairs on which this projection can operate, not including recursion. Derived classes should ensure that all contained projections are registered in the _projections set for the beam constraint chaining to work.
Definition at line 35 of file Projection.cc. {
set<PdgIdPair> ret = _beamPairs;
set<ConstProjectionPtr> projs = getProjections();
for (set<ConstProjectionPtr>::const_iterator ip = projs.begin(); ip != projs.end(); ++ip) {
ConstProjectionPtr p = *ip;
getLog() << Log::TRACE << "Proj addr = " << p << endl;
if (p) ret = intersection(ret, p->beamPairs());
}
return ret;
}
Determine whether this object should be ordered before the object p given as argument. If p is of a different class than this, the before() function of the corresponding type_info objects is used. Otherwise, if the objects are of the same class, the virtual compare(const Projection &) will be returned. Definition at line 24 of file Projection.cc.
Definition at line 143 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return _Bmax; }
Definition at line 144 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return _Bmin; }
Definition at line 145 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Use the projection manually (i.e. outside the projection mechanism) with raw 4-momentum inputs. Definition at line 34 of file Hemispheres.cc. {
MSG_DEBUG("Hemisphere axis = " << n);
MSG_DEBUG("Number of constituents = " << p4s.size());
FourMomentum p4With, p4Against;
double Evis(0), broadWith(0), broadAgainst(0), broadDenom(0);
foreach (const FourMomentum& p4, p4s) {
const Vector3 p3 = p4.vector3();
const double p3Para = dot(p3, n);
const double p3Trans = (p3 - p3Para * n).mod();
// Update normalisations
Evis += p4.E();
broadDenom += 2.0 * p3.mod();
// Update the mass and broadening variables
if (p3Para > 0) {
p4With += p4;
broadWith += p3Trans;
} else if (p3Para < 0) {
p4Against += p4;
broadAgainst += p3Trans;
} else {
// In the incredibly unlikely event that a particle goes exactly along the
// thrust plane, add half to each hemisphere.
MSG_WARNING("Particle split between hemispheres");
p4With += 0.5 * p4;
p4Against += 0.5 * p4;
broadWith += 0.5 * p3Trans;
broadAgainst += 0.5 * p3Trans;
}
}
// Visible energy squared.
_E2vis = sqr(Evis);
// Calculate masses.
const double mass2With = p4With.mass2();
const double mass2Against = p4Against.mass2();
_M2high = max(mass2With, mass2Against);
_M2low = min(mass2With, mass2Against);
// Calculate broadenings.
broadWith /= broadDenom;
broadAgainst /= broadDenom;
_Bmax = max(broadWith, broadAgainst);
_Bmin = min(broadWith, broadAgainst);
// Calculate high-max correlation flag.
const int maxMassID = (mass2With >= mass2Against);
const int maxBroadID = (broadWith >= broadAgainst);
_highMassEqMaxBroad = (maxMassID == maxBroadID);
}
Use the projection manually (i.e. outside the projection mechanism) with jet inputs. Definition at line 27 of file Hemispheres.cc.
Reset the projection. Definition at line 70 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Clone on the heap. Implemented in JetAlg, AxesDefinition, and ParticleFinder.
Compare with other projections. Implements Projection. Definition at line 93 of file Hemispheres.hh. {
return mkNamedPCmp(p, "Axes");
}
Register a contained projection (user-facing version)
Definition at line 151 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. { return declareProjection(proj, name); }
Register a contained projection. The type of the argument is used to instantiate a new projection internally: this new object is applied to events rather than the argument object. Hence you are advised to only use locally-scoped Projection objects in your Projection and Analysis constructors, and to avoid polymorphism (e.g. handling
Definition at line 142 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. {
const Projection& reg = _declareProjection(proj, name);
const PROJ& rtn = dynamic_cast<const PROJ&>(reg);
return rtn;
}
Clone on the heap.
Definition at line 103 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return _E2vis; }
Definition at line 104 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return sqrt(_E2vis); }
Get the named projection, specifying return type via a template argument (user-facing alias).
Definition at line 57 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. { return getProjection<PROJ>(name); }
Get a Log object based on the getName() property of the calling projection object. Reimplemented from ProjectionApplier. Definition at line 115 of file Projection.hh. {
string logname = "Rivet.Projection." + name();
return Log::getLog(logname);
}
Get the named projection, specifying return type via a template argument.
Definition at line 50 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. {
const Projection& p = getProjHandler().getProjection(*this, name);
return pcast<PROJ>(p);
}
Get the named projection (non-templated, so returns as a reference to a Projection base class). Definition at line 61 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. {
return getProjHandler().getProjection(*this, name);
}
Get the contained projections, including recursion. Definition at line 43 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. {
return getProjHandler().getChildProjections(*this, ProjectionHandler::DEEP);
}
Get a reference to the ProjectionHandler for this thread. Definition at line 122 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. {
return _projhandler;
}
Definition at line 112 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Definition at line 106 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return _M2high; }
Definition at line 109 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return _M2low; }
Definition at line 115 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Mark object as owned by the _projhandler
Definition at line 111 of file ProjectionApplier.hh. { _owned = true; }
Is the hemisphere with the max mass the same as the one with the max broadening? Definition at line 151 of file Hemispheres.hh. {
return _highMassEqMaxBroad;
}
Definition at line 113 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return sqrt(M2diff()); }
Definition at line 107 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return sqrt(M2high()); }
Shortcut to make a named Cmp<Projection> comparison with the Definition at line 47 of file Projection.cc. {
return pcmp(*this, otherparent, pname);
}
Shortcut to make a named Cmp<Projection> comparison with the
Definition at line 51 of file Projection.cc. {
return pcmp(*this, otherparent, pname);
}
Definition at line 110 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return sqrt(M2low()); }
Definition at line 116 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return sqrt(M2sum()); }
Get the name of the projection. Implements ProjectionApplier. Definition at line 102 of file Projection.hh. {
return _name;
}
Perform the projection on the Event. Implements Projection. Definition at line 8 of file Hemispheres.cc.
Definition at line 132 of file Hemispheres.hh. {
if (M2diff() == 0.0) return 0.0;
if (_E2vis != 0.0) return M2diff()/_E2vis;
else return std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
}
Definition at line 118 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Definition at line 125 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Definition at line 137 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return sqrt(scaledM2diff()); }
Definition at line 123 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return sqrt(scaledM2high()); }
Definition at line 130 of file Hemispheres.hh. { return sqrt(scaledM2low()); }
Used by derived classes to set their name. Definition at line 121 of file Projection.hh. Friends And Related Function Documentation
The Cmp specialization for Projection is a friend. Definition at line 36 of file Projection.hh.
Event is a friend. Definition at line 33 of file Projection.hh. Member Data Documentation
Flag to forbid projection registration in analyses until the init phase. Definition at line 176 of file ProjectionApplier.hh.
Hemisphere broadening variables. Definition at line 165 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Definition at line 165 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Visible energy-squared, Definition at line 159 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Is the hemisphere with the max mass the same as the one with the max broadening? Definition at line 168 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Hemisphere mass variables. Definition at line 162 of file Hemispheres.hh.
Definition at line 162 of file Hemispheres.hh. The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: Generated on Tue Dec 13 2016 16:32:48 for The Rivet MC analysis system by  1.7.6.1
1.7.6.1
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
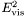 .
.  .
.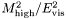 , is defined as
, is defined as ![\[ \frac{M^2_\mathrm{high}}{E^2_\mathrm{vis}} = \frac{1}{E^2_\mathrm{vis}} \max \left( \left| \sum_{\vec{p}_k \cdot \vec{n}_\mathrm{T} > 0} p_k \right|^2 , \left| \sum_{\vec{p}_k \cdot \vec{n}_\mathrm{T} < 0} p_k \right|^2 \right) \]](form_38.png)
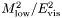 , is the sum of momentum vectors in the opposite hemisphere, i.e.
, is the sum of momentum vectors in the opposite hemisphere, i.e. 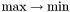 in the formula above.
in the formula above.![\[ \frac{M^2_\mathrm{diff} }{ E^2_\mathrm{vis}} = \frac{ M^2_\mathrm{high} - M^2_\mathrm{low} }{ E^2_\mathrm{vis}} . \]](form_41.png)
![\[ B_\pm = \frac{ \sum{\pm \vec{p}_i \cdot \vec{n}_\mathrm{T} > 0} |\vec{p}_i \times \vec{n}_\mathrm{T} | }{ 2 \sum_i | \vec{p}_i | } \]](form_42.png)
![\[ B_\mathrm{max} = \max(B_+, B_-) \]](form_43.png)
![\[ B_\mathrm{min} = \min(B_+, B_-) \]](form_44.png)
![\[ B_\mathrm{sum} = B_+ + B_- \]](form_45.png)
![\[ B_\mathrm{diff} = |B_+ - B_-| \]](form_46.png)